A small number of people have early-onset Alzheimer disease which starts when they are in their 30s or 40s. However some with the disease live two decades or more.
 Molecules Free Full Text The Role Of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor In Alzheimer S Disease Conventionally Pathogenetic Or Unconventionally Protective Html
Molecules Free Full Text The Role Of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor In Alzheimer S Disease Conventionally Pathogenetic Or Unconventionally Protective Html
Alzheimer disease is becoming more common as the general population gets older and lives longer.

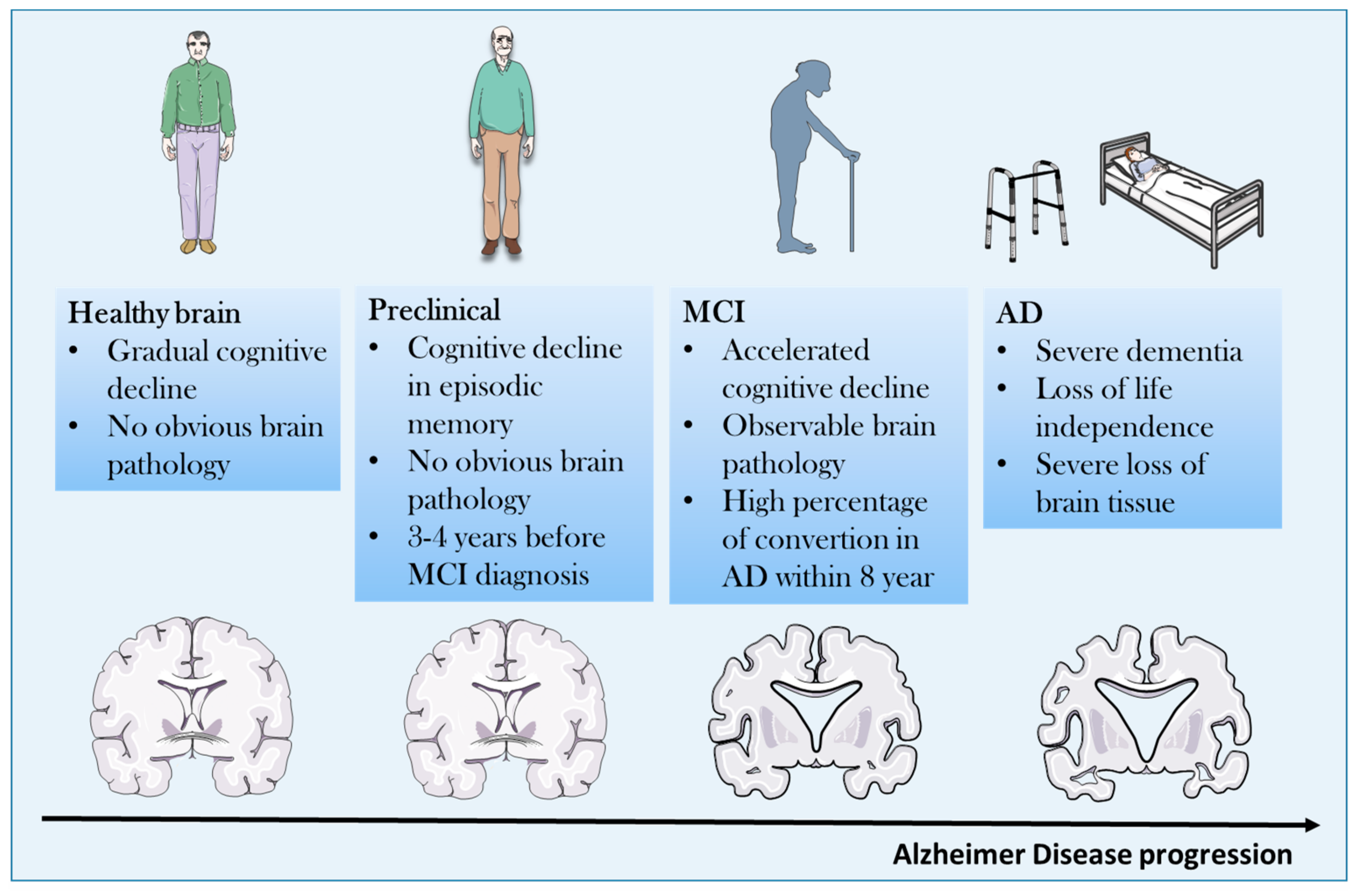
Progression of alzheimer's disease. The patient may then progress through mild moderate and severe AD dementia. Each person is unique and experiences dementia in their own way. Both transcript and protein data indicate that cholinotrophic neuronal dysfunction is related to an imbalance between TrkA-mediated survival signa.
However the ventricles chambers within the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid are noticeably enlarged. 4 rijen Alzheimers is a progressive disease with people living an average of four to eight years. The number of patients with Alzheimers disease AD has been increasing exponentially side by side with aging societies worldwide.
For this purpose metal content was analyzed after size-fractionation of species and then inter-element and inter-fraction ratios were computed. Early Stages of Alzheimers. A persons age for example Alzheimers disease generally progresses more slowly in older people over 65 than in younger people under 65 other long-term health problems dementia tends to progress more quickly if the person is living with other conditions such as heart disease diabetes or high blood pressure particularly if these are not well managed.
Alzheimer disease usually affects people older than 65. In order to study the involvement of metals in the progression of Alzheimers disease serum samples from patients with Alzheimer and mild cognitive impairment were investigated. How quickly dementia progresses depends on the individual.
But its speed of progression varies depending on a persons genetic makeup environmental factors age at diagnosis and other medical conditions. People live for an average of 8 years after their symptoms appear. The Progression of Alzheimers Disease and Resource use PADR study is a longitudinal observational study with assessments at the time of diagnostic workup baseline and follow-up after a mean of 24 months range 1637 80 between 20 and 28 months.
In the early stages of Alzheimers disease short-term memory begins to decline when the cells in the hippocampus degenerate. It involves a gradual loss of memory as well as changes in behavior thinking and language skills. Alzheimers typically follows certain stages that bring about different changes in that persons life as well as the lives of their family members.
This means that the structure and chemistry of the brain become increasingly damaged over time. Advertentie Inviting original research advancing our understanding of protein misfolding clearance. Alzheimers disease is a progressive neurocognitive disorder that becomes worse over time.
The earliest stages of Alzheimers disease are the preclinical stage followed by mild cognitive impairment MCI due to AD. Yes Alzheimers disease usually worsens slowly. Stages of Alzheimers Overview of disease progression Early-stage Alzheimers mild Middle-stage Alzheimers moderate Late-stage Alzheimers severe.
Symptoms of AD worsen over time due to progressive neurodegeneration requiring institutional care at the later stage and resulting in a heavy burden on patients caregivers and the public-health system. Advertentie Inviting original research advancing our understanding of protein misfolding clearance. The progression rate for Alzheimers disease can vary widely.
Alzheimers Symptom Progression. Learn about the progression of Alzheimers disease AD. Alzheimers disease is a brain disease where brain cells progressively degenerate.
As Alzheimers disease progresses brain tissue shrinks. According to the Mayo Clinic people who have been diagnosed with Alzheimers disease average between three and 11 years after diagnosis. All types of dementia are progressive.
The current review summarizes the pathobiology of nerve growth factor NGF and its cognate receptors during the progression of Alzheimers disease AD. Including interventions directed at reducing protein aggregates. Including interventions directed at reducing protein aggregates.
Progression from stage to stage.


